Getting started with Rich Text
Enabling the Rich Text
- Select the desired content type from the Content model tab.
- Create a new field by clicking Add field and select Rich Text as the field type.
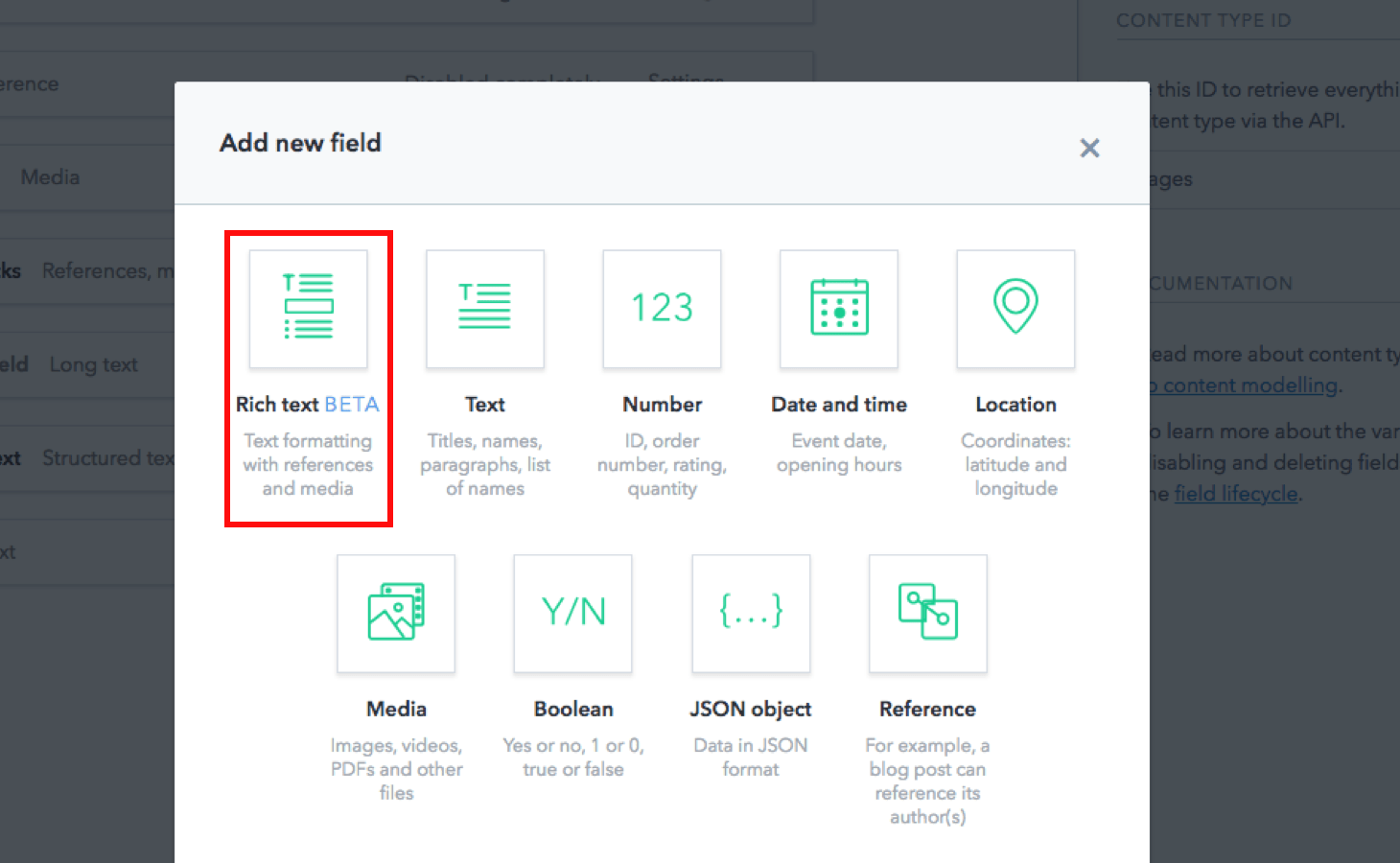
Customize the formatting options
Customization assists in selecting relevant options for the authors in the toolbar while using the Rich Text editor. It can be done with an API call or on the Web App.
Customization with an API call
A content type using Rich Text can be customized by making a Content Management API (CMA) call.
For example, following is the API call to only allow paragraphs and specific formatting in them:
{
"id": "YOUR_CONTENT_TYPE_ID",
"name": "Rich Text Field",
"type": "RichText",
"validations": [
{
"enabledNodeTypes": ["paragraph", "text"],
"message": "Please choose a valid node type (should be a paragraph or text)."
},
{
"enabledMarks": ["bold", "italics"],
"message": "Please remove any extraneous document markup - only bold and italics are supported."
}
]
}Similarly, to limit the type of content types that an author could hyperlink to:
{
"id": "YOUR_CONTENT_TYPE_ID",
"name": "Rich Text Field",
"type": "RichText",
"validations": [
{
"enabledNodeTypes": [
"paragraph",
"text",
"entry-hyperlink"
],
"message": "Please choose a valid node type (should be a paragraph, hyperlink or text)."
},
{
"nodes": {
"entry-hyperlink": [
{
"linkContentType": [
"page"
],
"message": "You can only hyperlink to Pages."
}
]
}
}
]
}Refer to the CMA reference to learn more about the other available validation options.
Customization on Web app
To customize the field on the Web App:
- Select the desired content type from the Content model tab.
- Edit the Rich Text field's Settings and select the relevant formatting options.
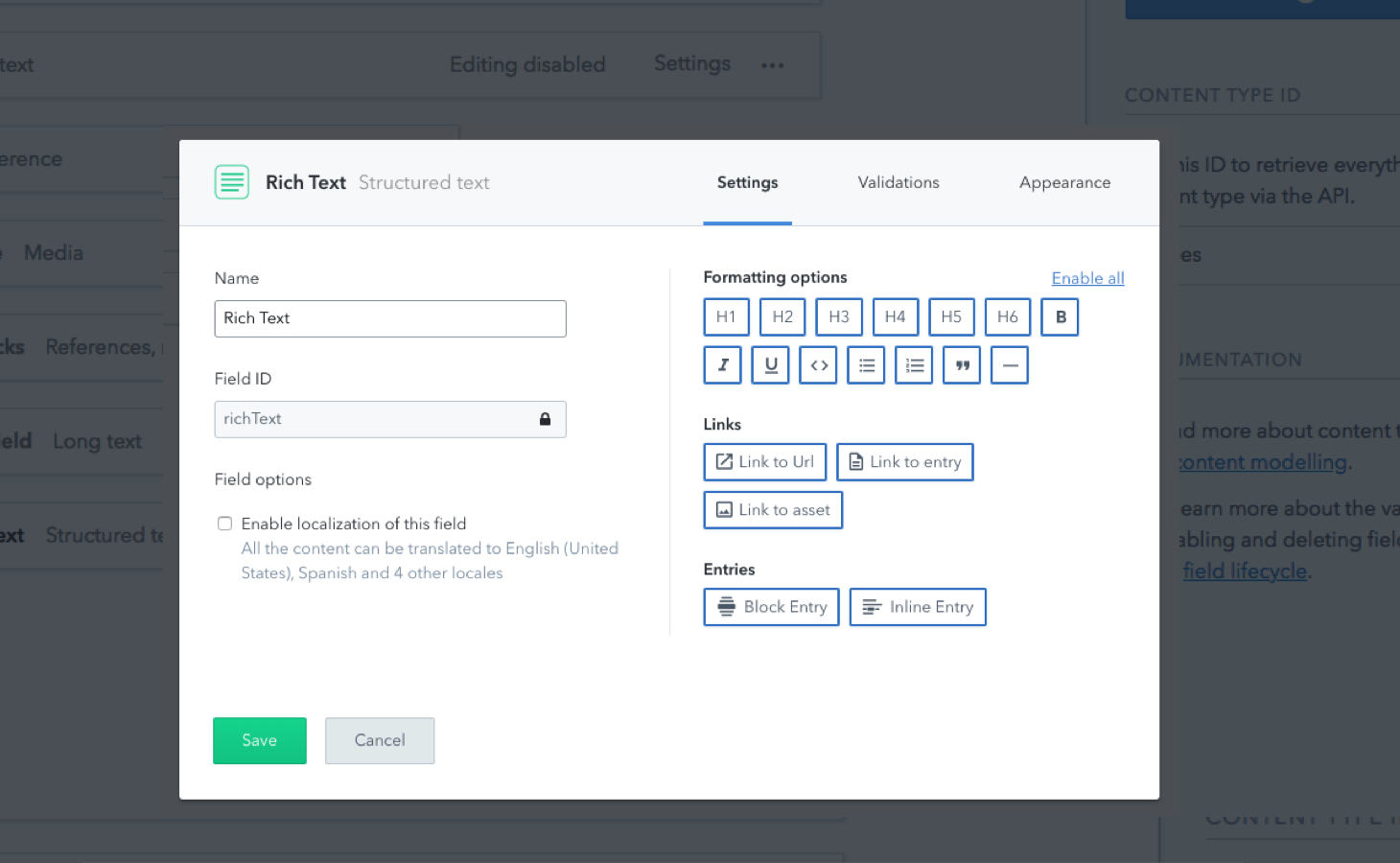
Render the response in HTML
The content added to the Rich Text field can be consumed from the API response and rendered further in the desired application.
Rendering the API response (a JSON object) is not easy and requires effort to be converted to HTML. Hence, helper functions are created that allow to:
- Render all the contents of a JSON response to HTML.
- Apply a custom rendering function to an embedded entry.
- Apply a custom rendering function to a default node, like a heading or a link, thereby applying personalized style and logic to the markup of an application.
Use-cases around rendering the API response
Add custom CSS classes to HTML elements
Following is an example of adding CSS classes to paragraph tags in JavaScript in order to alternate their background color:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { BLOCKS } from '@contentful/rich-text-types';
import { documentToReactComponents } from '@contentful/rich-text-react-renderer';
const richTextDocument = {
nodeType: 'document',
data: {},
content: [
{
nodeType: 'paragraph',
content: [
{
nodeType: 'text',
marks: [],
value: 'I am an odd paragraph.',
data: {}
}
],
data: {}
},
{
nodeType: 'paragraph',
content: [
{
nodeType: 'text',
marks: [],
value: 'I am even.',
data: {}
}
],
data: {}
}
]
};
const options = {
renderNode: {
[BLOCKS.PARAGRAPH]: (node, children) => (
<p className={paragraphClass(node)}>{children}</p>
)
}
};
function paragraphClass(node) {
const className = 'odd';
//alternate logic for 'odd' | 'even'
return className;
}
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
ReactDOM.render(
documentToReactComponents(richTextDocument, options),
rootElement
);
// -> <p class='odd'>I am an odd paragraph.</p>
// -> <p class='even'>I am even.</p>Link to entries
Following is an example of how to render links to entries:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { INLINES } from '@contentful/rich-text-types';
import { documentToReactComponents } from '@contentful/rich-text-react-renderer';
const richTextDocument = {
nodeType: 'document',
data: {},
content: [
{
nodeType: 'paragraph',
content: [
{
nodeType: 'entry-hyperlink',
data: {
target: {
sys: {
type: 'Link',
linkType: 'Entry',
id: '3vNbx1hjcsESSICSu2KuWs'
}
}
},
content: [
{
nodeType: 'text',
marks: [],
data: {},
value: "I'm linking to an entry"
}
]
}
],
data: {}
}
]
};
const options = {
renderNode: {
[INLINES.ENTRY_HYPERLINK]: (node, children) => {
// If you are using contenful.js sdk, the referenced entry is resolved
// automatically and is available at `node.data.target`.
const referencedEntry = getEntryWithId(node.data.target.sys.id);
return <a href={`/pages/${referencedEntry.fields.slug}`}>{children}</a>;
}
}
};
function getEntryWithId(entryId) {
const mockEntry = {
fields: {
slug: 'entry-slug'
}
};
return mockEntry;
}
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
ReactDOM.render(
documentToReactComponents(richTextDocument, options),
rootElement
);
// <a href='/pages/entry-slug'>I'm linking to an entry</a>Render custom widgets
Following is an example to render a custom widget, such as a Carousel, within your flow of text, in JavaScript:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { BLOCKS } from '@contentful/rich-text-types';
import { documentToReactComponents } from '@contentful/rich-text-react-renderer';
const richTextDocument = {
nodeType: 'document',
data: {},
content: [
{
nodeType: 'embedded-entry-block',
data: {
target: {
sys: {
type: 'Link',
linkType: 'Entry',
id: '3vNbx1hjcsESSICSu2KuWs'
}
}
},
content: []
}
]
};
const options = {
renderNode: {
[BLOCKS.EMBEDDED_ENTRY]: node => <CustomCarousel node={node} />
}
};
function CustomCarousel({ node }) {
// Render the Carousel component from your Component Library
return <div />;
}
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
ReactDOM.render(
documentToReactComponents(richTextDocument, options),
rootElement
);
// <CustomCarousel />Get started with various platforms
The helper functions are available for the following platforms: